How To Splice Fiber Optic Cables
How To Splice Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cabling is the neural network of modern society, carrying everything from breaking news to that meme you liked on Instagram last night. It is what powers internal servers and modern Internet connections, resulting in faster speeds than ever. Thanks to fiber splicing, when fiber breaks, that endless flood of data does not need to stop.
Before we can explain how to splice fiber optic cables, we need to establish what splicing is as well as the different methods.
What Is Fiber Splicing?
Fiber optic splicing is the process of joining two different fiber optic cables and creating one functioning cable. When done correctly, splicing creates a cable with improved durability and minimal loss.
The two most common methods of fiber splicing are mechanical and fusion. Both perform the same function, but the procedures differ greatly.
Mechanical Splicing Vs. Fusion Splicing
There are many factors to consider when choosing which type of fiber splicing to perform. One is simpler, but the other is more precise. Read on to learn the details.
Mechanical Splicing
A mechanical splice aligns two or more cleaved fiber tips and keeps the fibers together with an assembly, usually a plastic snap-type cover. Mechanical splicing takes much less time and effort, using no power supplies and very few tools. However, a mechanical splice is often considered temporary and can cause an insertion loss of about 0.3 dB, meaning light will pass through a little less efficiently than before.
Fusion Splicing
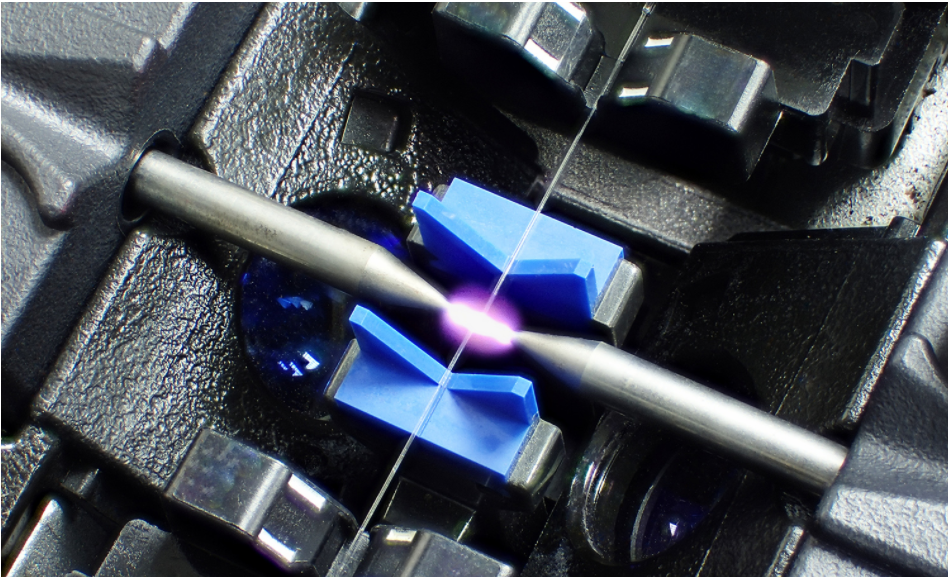
Fusion splicing is the most used method of fiber optic splicing and the main one we will discuss. Rather than using a cover to align the cables, this method involves heating and melting the ends together. This creates a much more durable connection that can reduce loss to 0.02 dB. Between increased durability and improved performance, technicians usually opt to use a fusion splicer when possible.
Fusion splicing is also the most reliable method for single-mode fibers. Different from multimode fibers, single-mode fibers have a thin core that transmits signals without touching the fiber’s edges. Since fusion splicing won’t alter the fiber’s structure, it is recommended for long-term fixes.
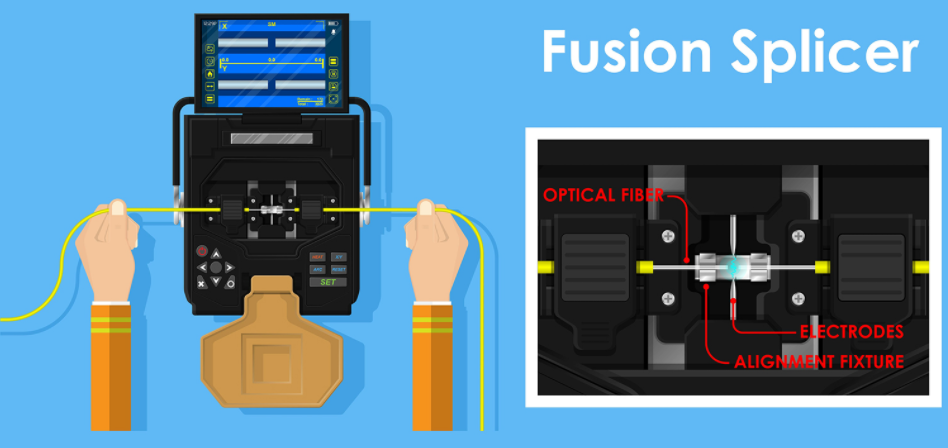
How Does Fusion Splicing Work?
Using cameras to align the two fiber ends and clean them of dust or dirt, a fusion splicer provides heat from an electrical arc to weld the ends together, then further tests the integrity of the weld by giving the fiber a tug.
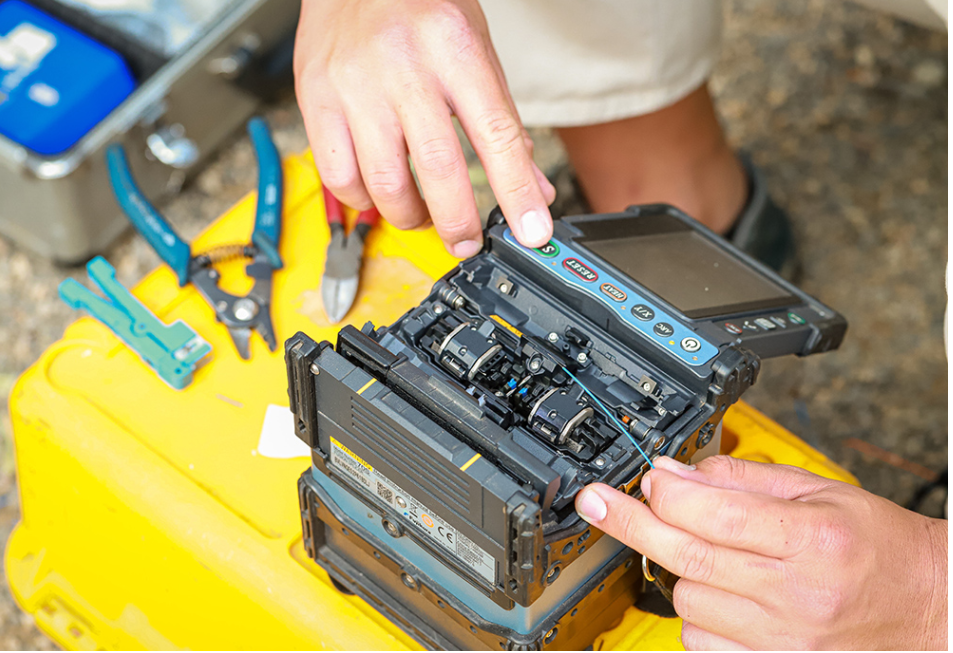

How To Splice Fiber Optic Cables
Thanks to technological advancements, this complicated process can be broken up into a handful of simple steps:
1:Strip the Fibers: Before fusing, remove the cable jacket and coating. Using a tool like a mechanical fiber stripper, reduce the coating and exterior until all that is left are bare fiber cores.
2:Clean the Fibers: Although a fusion splicer will burn off impurities before the fusion, the fibers need to be cleaned in the case of any contaminants residing further down the line. Carefully applying a fiber optic cleaning solution should remove most dust or particles.
3:Cleave the Fibers: This step requires the most precision. Using a fiber cleaver, carefully create a break within the fiber with ends that are perpendicular to the fiber axis.
4:Align the Fibers: If using a splicer with automatic alignment, simply place the fiber ends within the device’s holder. For splicers with manual alignment, match the fiber end faces so the electrodes are centered.
5:Fuse the Fibers: The device will weld the two ends together, then test to make sure they are securely joined.
6:Protect the Splice: Once the fusion has been inspected, apply a heat-shrink sleeve around the newly fused area to protect it from contamination. Some splicers may do this automatically.